A Twisted Pelvis, Also Called Pelvic Torsion, Can Be Corrected
Shedding light on Unexplained Pain and steps you can take for lasting relief
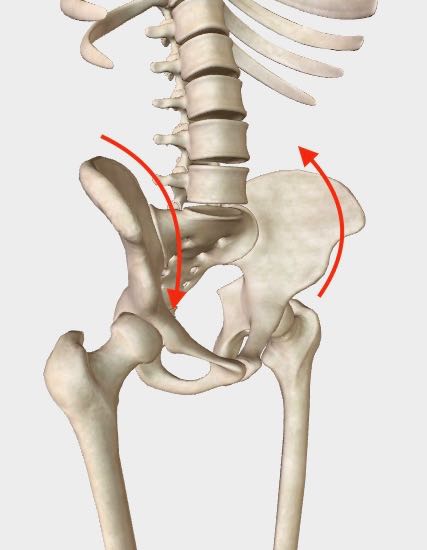 A twisted pelvis, also known as pelvic torsion.
A twisted pelvis, also known as pelvic torsion.What is pelvic Torsion (aka a twisted Pelvis)?
A twisted pelvis, also known as pelvic torsion, is an extremely common distortion pattern but often remains undiagnosed. The result can be significant chronic pain that seems to have no clear explanation.
Without understanding this phenomenon, it's impossible to see the cascading muscular effects that can result.
Back pain, hip pain, knee pain, shoulder pain, neck pain, and more can potentially be traced back to this primary root cause.
To help us understand what we mean by a twisted pelvis or pelvic torsion it’s helpful to have a clear sense of the bony anatomy of the pelvis.
The pelvis is composed three bones:
- Two pelvic bones, the right ilium and left ilium
- The sacrum
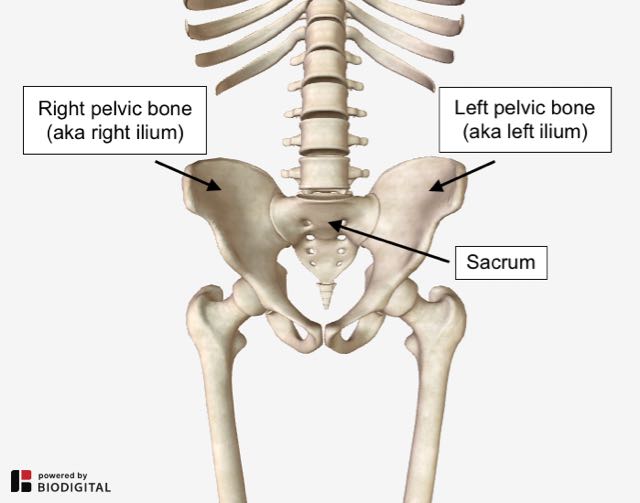 Pelvic bones and sacrum.
Pelvic bones and sacrum.What do we mean by, Torsion?
To understand what we mean by torsion, let’s look to Miriam-Webster:
torsion1: the twisting or wrenching of a body by the exertion of forces tending to turn one end or part about a longitudinal axis while the other is held fast or turned in the opposite direction also : the state of being twisted 2: the twisting of a bodily organ or part on its own axis 3: the reactive torque that an elastic solid exerts by reason of being under torsion |
Pelvic Torsion (a twisted pelvis), then, is a condition in which one pelvic bone is twisting in one direction and the other pelvic bone is either 1) fixed in place or 2) is twisting in the opposite direction.
In the example below, the arrows indicate the rotational direction of this twisting motion.
Here, the torsion is an anterior (or forward) rotation of the right pelvic bone, with the left pelvic bone in an oppositional rotation.
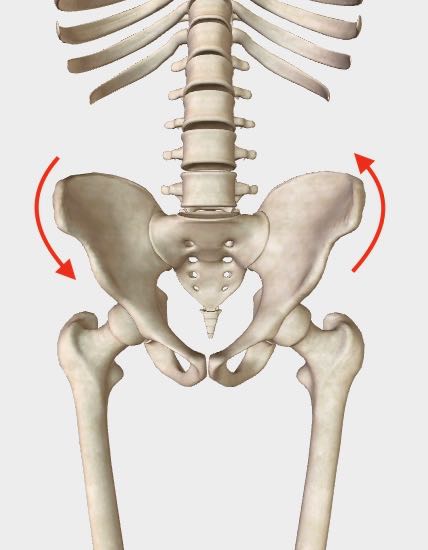 Right anterior, left posterior pelvic rotation, front view. Right anterior, left posterior pelvic rotation, front view. |
 Right anterior, left posterior pelvic rotation, quarter angle view. Right anterior, left posterior pelvic rotation, quarter angle view. |
NOTE - The images here don't show the actual position of the pelvic bones in a torsion pattern because the imaging I’m using doesn’t have this flexibility. Therefore the bones, here, are in a neutral position. The red arrows are meant to imply the torsion pattern.
"No amount of symptomatic treatment can have any lasting value without correcting the pelvic torsion pattern."
Impact on the body
The immediate impact of pelvic torsion (a twisted pelvis) is to change the height of the hip joints in relation to one another.
In other words, the hip joints are no longer level. One hip joint is positioned higher and the other is positioned lower.
The result is a FUNCTIONAL leg length discrepancy.
Understanding a functional leg length DISCREPANCY
When a pelvis is balanced, the hip joints are level and the legs are more or less equal in length. (Except in cases of trauma, surgery or congenital defect.)
When there’s a torsion, one hip joint is pulled up higher than the other causing a functional leg length discrepancy.
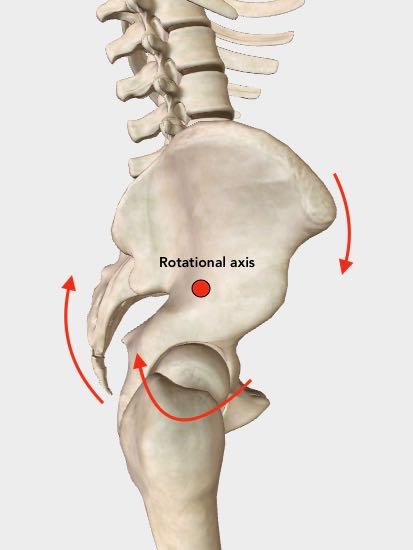 Right anterior rotation with rotational axis shown.
Right anterior rotation with rotational axis shown.In this example, a right anterior (forward) rotation has the effect of pulling the right hip joint upwards.
If you look closely at the right hip joint perhaps you can see how this happens.
Can you visualize how a right rotation around the rotational axis would elevate the right hip joint? And how that would result in the entire right leg being pulled upward?
The overall result is that the entire right leg becomes functionally short.
This does not mean that one leg is actually shorter than the other.
This is an example of a functional leg length discrepancy, as distinct from a congenital leg length discrepancy.
not the same as a congenital or anatomical leg length discrepancy
A congenital leg length discrepancy is one we're born with and in which the leg bones themselves are a different length.
A congenital leg length discrepancy is routinely and appropriately addressed with a shoe lift of some kind.
A shoe lift, however, should not be used as a solution for addressing a functional leg length discrepancy as it would simply lock the imbalance in place.
As we will see, a functional leg length discrepancy can be corrected — i.e. brought back into balance — while a congenital leg length difference can only be compensated for.
How does a leg length discrepancy result in pain?
When the legs are a different length, our balance is disrupted whenever we’re upright in gravity. In other words, the body has to do a lot of extra work in order to hold itself upright.
We refer to the event of being knocked off our center of gravity as a loss of equipoise. This is also referred to as a loss of verticality or loss of alignment, and this can be a root cause of an array of potential problems.
Equipoise in the body is the state in which, when we’re upright, no muscles are compelled to continuously brace in opposition to the force of gravity.
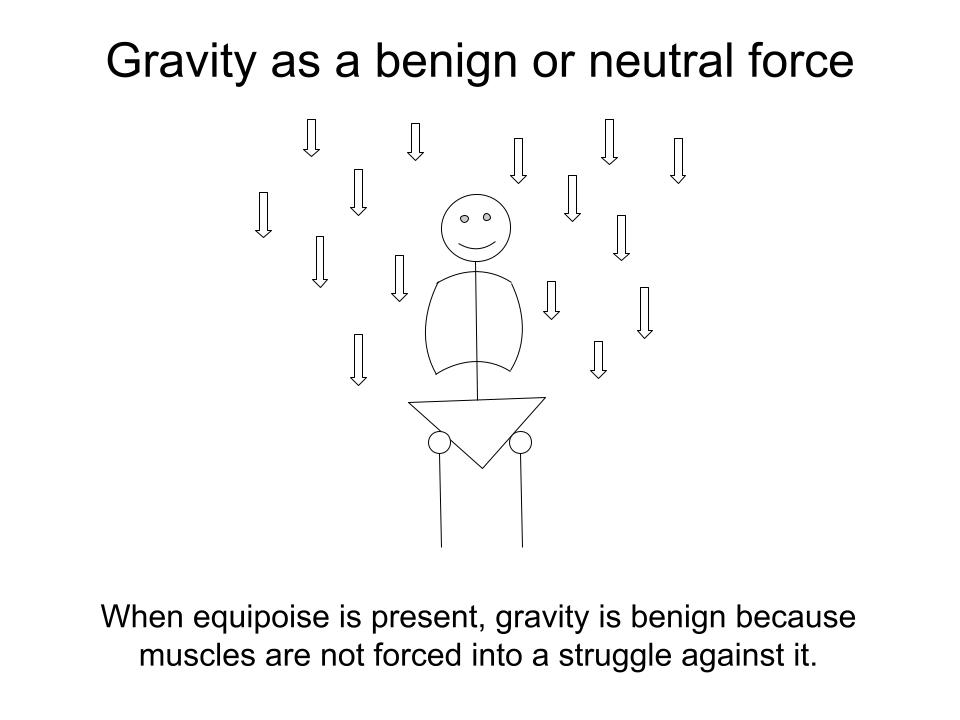
When the body is in equipoise:
- Muscles appropriately respond to movement by contracting and relaxing, over and over, thousands of times.
- No muscular bracing is required to hold the body upright.
- Gravity is a benign or neutral force passing through the body’s structure.
But when equipoise is disrupted, a complex array of compensations can result.
The following examples demonstrate this disruption.
"S" Curve in the spine
Here a functionally short right leg is shown to initiate a back-and-forth muscular counter-balancing that results in an “S” Curve in the spine.
The body’s automatic response to the short right leg in Figure 1 is to contract muscles on the opposite side, shown in Figure 2, as a counter-balance.
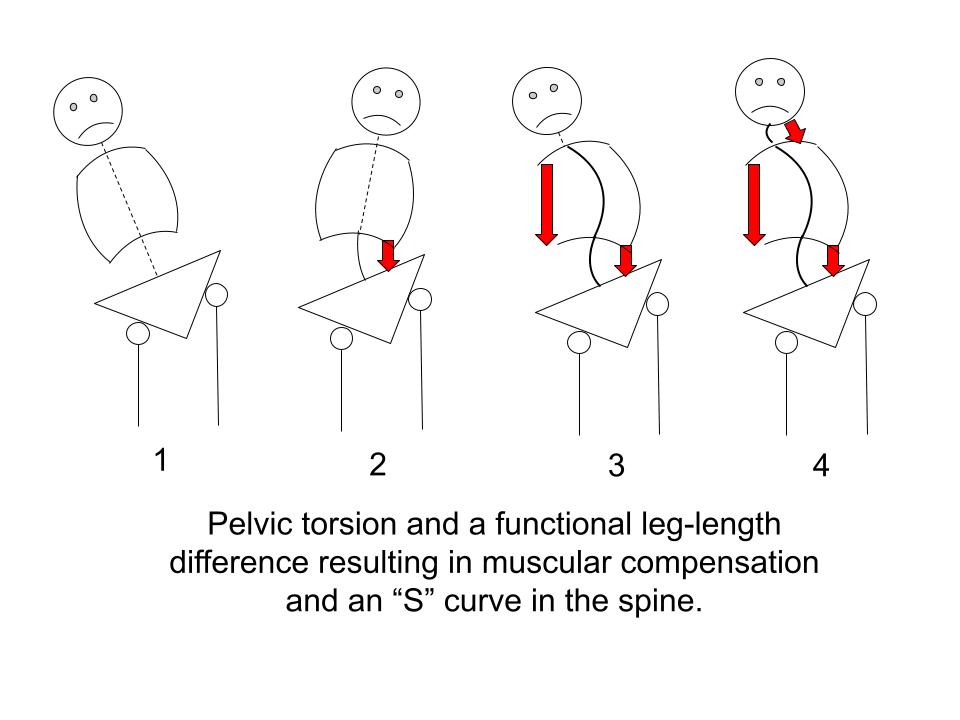
But the muscular response in Figure 2 pulls the body too far in the opposite direction thus triggering the need for another counter-balance, shown in Figure 3.
In Figure 3 the head has been pulled too far to the right and a final counter-balance is needed to bring the head more or less upright, shown in Figure 4.
The result is an “S” curve in the spine and a series of muscular compensations in which muscles are forced to brace in order to hold the body upright.
"C" CURVE IN THE SPINE
In the following, we see how this muscular counter-balancing can result in a “C” curve in the spine.
The compensation for the short right leg in Figure 1 is shown in Figure 2 where the entire torso on left engages as a counter-balance.
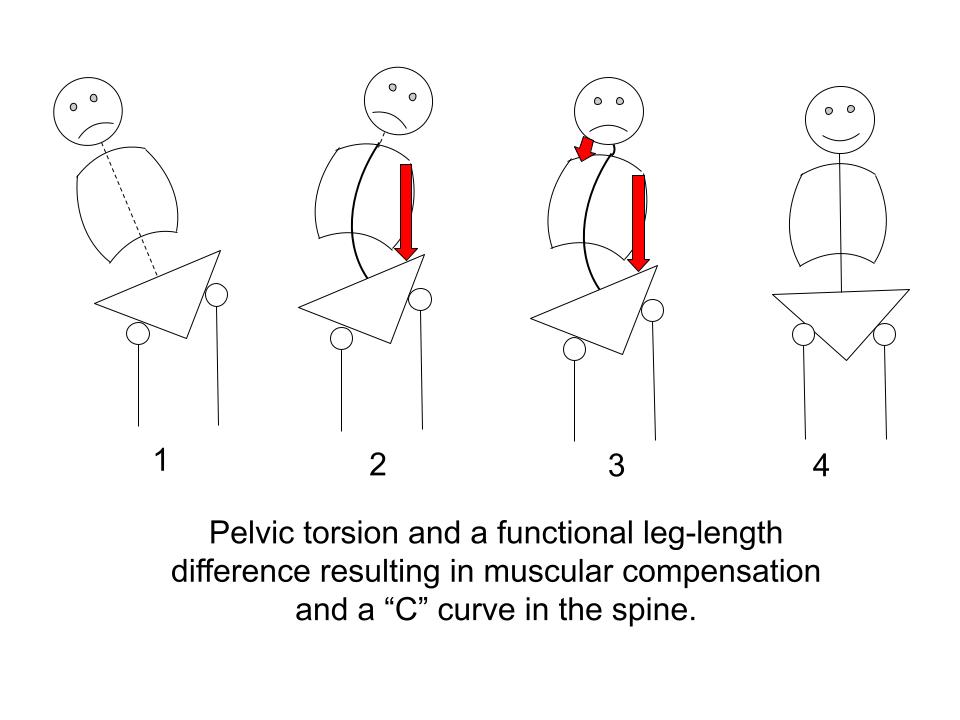
But in Figure 2 the head is pulled too far to the left.
This triggers the need for the counter-balancing shown in Figure 3 where the neck muscles compensate to bring the head more or less upright.
(Figure 4 is enjoying equipoise.)
When equipoise is lost
To summarize, when equipoise is lost:
- The body shifts from being in a neutral relationship with gravity to being in a struggle with it.
- Our muscular system is automatically triggered to bring us upright, resulting in compensations.
Over time, these compensations can become the source of significant pain and dysfunction in the body.
How?
Certain muscles become locked short -- which means tight, braced, stuck -- while other muscles become locked long -- which means strained, overstretched, weakened.
locked short and locked long muscles
The muscular compensation such as is shown the “S” curve and “C” curve examples results in two opposite muscular effects:
1. Some muscles are forced to strongly contract
This is suggested by the red arrows above. A shortened or shortening muscle will always be found in the CONCAVE part of the curve.
Over time, shortened muscles can become chronically tight, braced and ischemic (reduced blood flow).
I refer to these muscles as Locked Short.
2. Some muscles are forced to lengthen or overstretch
What’s not emphasized in the images above is the CONVEX side of the curve where muscles are forced to lengthen.
Over time, muscles that are constantly forced to lengthen can become overstretched, strained, weak and ischemic (reduced blood flow).
I refer to these muscles as Locked Long.
Perhaps you can visualize the strain on the muscles on the CONVEX side of the curve where they are forced into a chronically overstretched position.
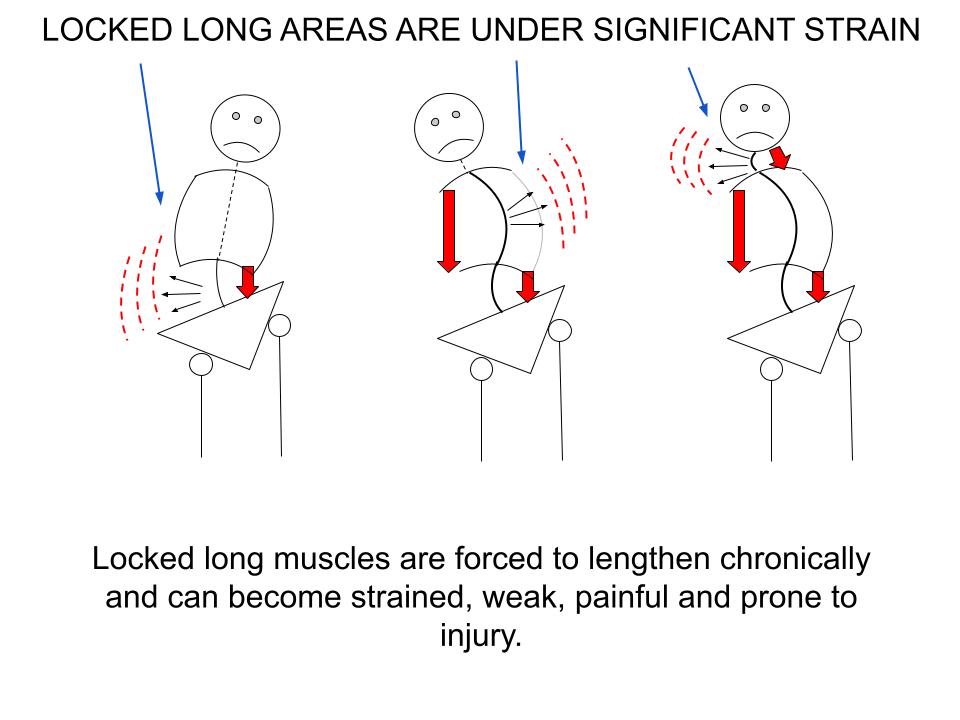
Understanding the characteristics of -- and differences between -- locked short and locked long muscles is not only essential in diagnosing pain, but also for resolving it --quickly, efficiently and without aggravating symptoms.
THE QUALITY OF PAIN IS NOT THE SAME IN LOCKED SHORT AND LOCKED LONG MUSCLES
For example, the pain felt in a locked short muscle will often be described as deep or aching or felt in a broad area. The impulse to grab or press on the muscle is common because that feels somewhat relieving.
The discomfort in a locked short muscle can often be improved by:
- Strong direct pressure, like deep massage techniques
- Comprehensive, deep stretching
- Rigorous movement, activity, exercise
On the other hand, the pain felt in a locked long muscle tends to be sharp, intense or burning.
Instead of covering a broad area, it’s often more focused. I’ve heard it described like a knife jabbing the area.
Sometimes it has a "tearing" feeling.
Often it feels as if the muscle is extremely vulnerable, like it might go into spasm if you move wrong.
Because of this fragile quality, the worst, most intense, most intractable pain is often located in locked long muscles.
That’s not to say that pain in a locked short muscle can’t produce significant pain. It certainly can. Locked short muscles are often the site of myofascial trigger points which can cause radiating or referred pain, for example.
But it’s easier to bring some temporary relief to a locked short muscle using one of the strategies listed above.
Locked long muscles do not respond positively to these treatment strategies.
In fact, using strong or deep direct pressure or comprehensive deep stretching or rigorous movement, activity or exercise — can significantly aggravate and sometimes further injure a locked long muscle.
Because locked long muscles are overstretched, strained, weak and, over time, worn down, such muscles can become, as we’ve said, fragile. It doesn’t want strong stimulation and must be treated gently.
This distinction is critical to understand because otherwise every muscle and every pain is treated the same way.
Where strong, assertive treatment can be helpful for a tight, stuck, locked short muscle, treatment for a strained, locked long muscle should be limited to gentle mobilization and, in some cases, very gentle hands-on massage treatment.
But the only way to truly relieve the strain and pain in a locked long muscle — and to do so in a lasting way — is to get that muscle out of its overstretched, strained position.
By the same token, the only way to get a locked short muscle to let go of its persistent grip of chronic tightness in a lasting way is to restore equipoise and remove the struggle against gravity.
the potential cascade of effects from pelvic torsion
A twisted pelvis, pelvic torsion, results in...
⇣
A functional leg-length difference, which causes...
⇣
Loss of equipoise or vertical alignment, that results in…
⇣
An involuntary muscular response in the body to hold itself upright in gravity, resulting in…
⇣
Certain muscles becoming locked short, fixed, chronically tight and stuck…
⇣
While other muscles become locked long, strained, weakened and prone to injury.
⇣
These imbalances can lead to:
• Ischemia (reduced blood flow)
• Myofacial trigger points
• Fascial shortening
• Distorted joint movement
• And many other problems
All of which can be the source of…
⇣
Pain or symptoms that cannot be accounted for by X-rays, MRIs, CAT scans or any allopathic testing.
Cause of pelvic torsion - part 1
The immediate trigger
Back in the mid 1990’s when I was first learning about pelvic torsion, aka a twisted pelvis, we were taught a variety of mobilization techniques to correct it.
We would literally get a hold of the rotated pelvis and use a corkscrew technique to bring it back into balance. We would also perform mobilization techniques to free-up the sacroiliac joints and hip joints as these were thought to be contributing or reinforcing factors.
These mobilization techniques worked to a degree; in the moment you could observe a positive change and relief could be felt. But what I found was that the correction wouldn’t last. And for some the mobilization techniques alone didn’t really work at all.
As I continued to research this problem in my clinical practice, I found myself focusing more and more on a set of muscles which occupy the very core of our bodies: the primary hip flexor muscles.
Our primary hip flexors are the iliacus muscle and the psoas muscle.
These two muscles are collectively referred to as the iliopsoas because they share a common attachment at the upper inner thigh. But they are distinct muscles with different starting points.
The psoas has its origin along the lumbar spine, while the iliacus has its origin on the inner part of the pelvic bone (called the iliac fossa).
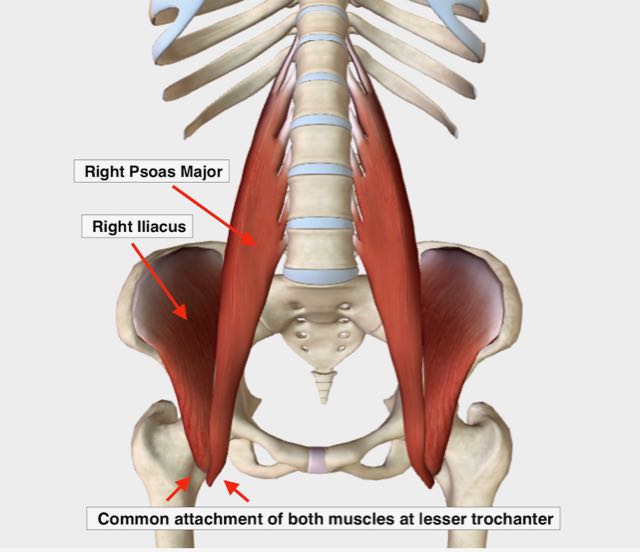
What I started noticing was that the muscular pattern I routinely saw when pelvic torsion was present was this:
The iliacus on one side and the psoas on the other side were both locked short.
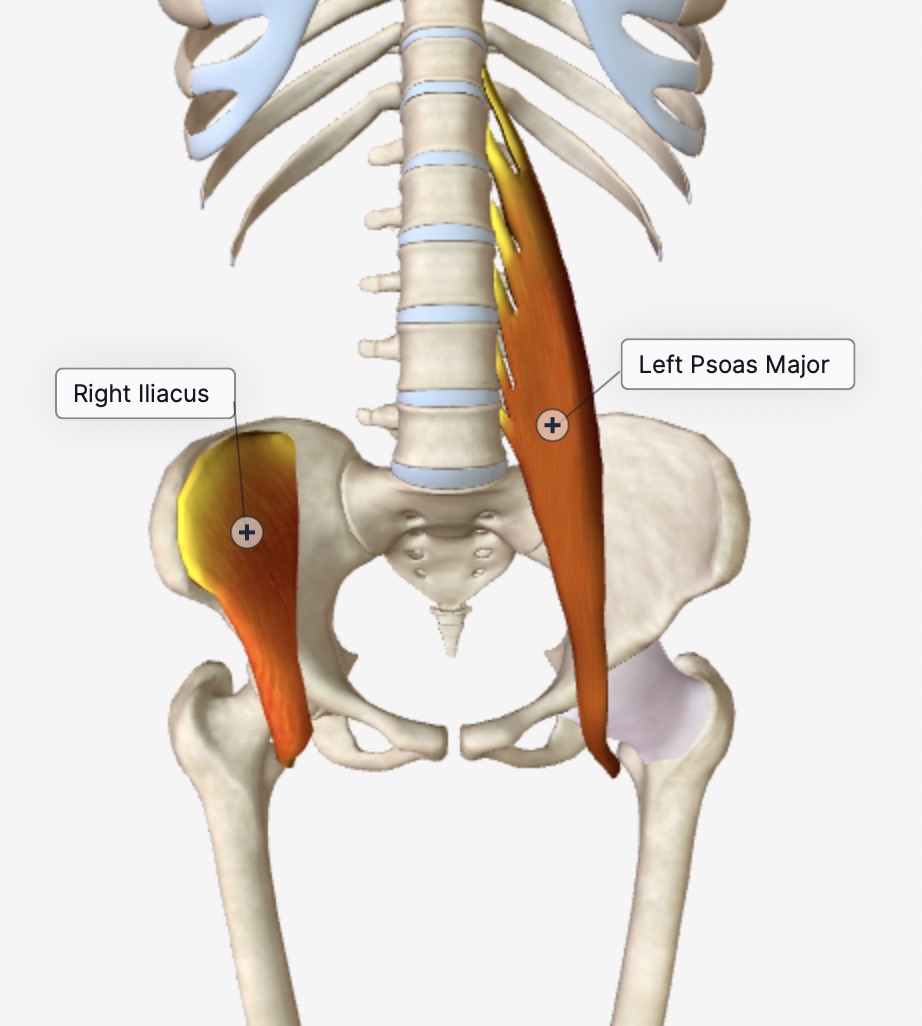 Right iliacus and left psoas major.
Right iliacus and left psoas major.See if you can visualize this.
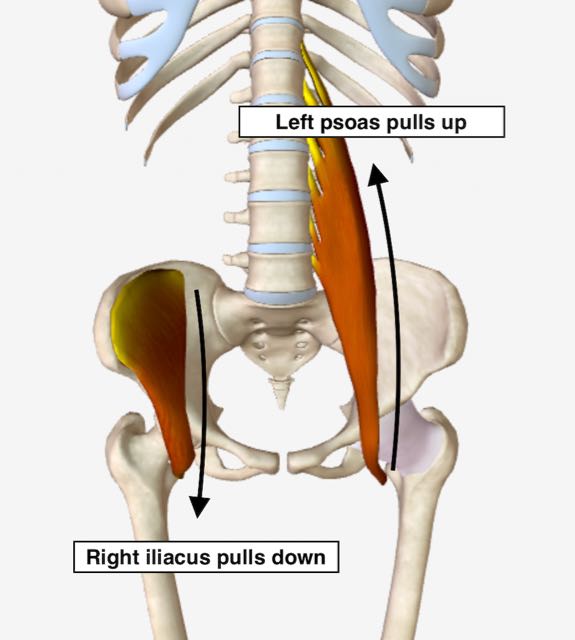 Right iliacus and left psoas both locked short.
Right iliacus and left psoas both locked short.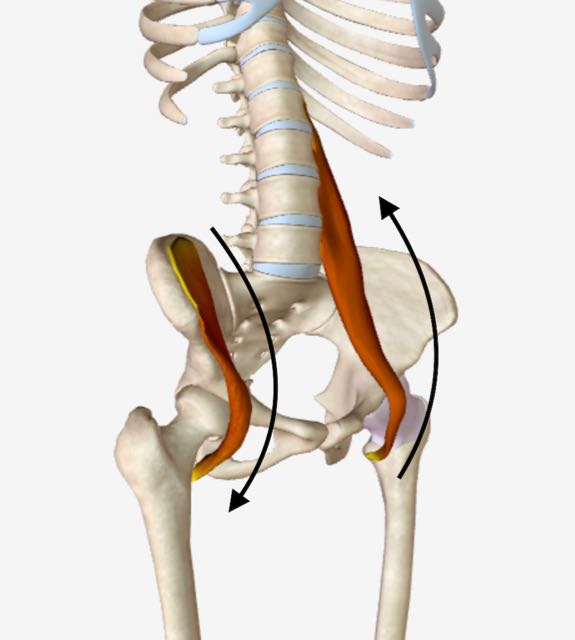 Right iliacus and left psoas both locked short, quarter angle view.
Right iliacus and left psoas both locked short, quarter angle view.In this example, a locked short right iliacus pulls down causing the hip bone to rock forward. The result is that the right pelvic bone gets positioned in an anterior, or forward, rotation.
Simultaneously, a locked short left psoas pulls up causing the left pelvic bone to become fixed in place and unable to rotate forward.
The result is that the right and left hip bones become stuck in oppositional rotation (resulting in a leg-length difference, loss of equipoise, etc).
Thus, the immediate trigger for pelvic torsion is:
Dysfunction of the primary hip flexor muscles, the iliacus and psoas, collectively referred to as the iliopsoas.
CAUSE OF PELVIC TORSION - PART 2
the UNDERLYING CAUSES
Having understood the immediate trigger (proximate cause) for pelvic torsion, aka a twisted pelvis, to be a type of hip flexor dysfunction, I now wanted to answer this question:
What were the "big picture" forces that caused hip flexor dysfunction in the first place?
the three "BIG PICTURE" FORCES CAUSING HIP FLEXOR DYSFUNCTION and a twisted pelvis
Unlike most muscles in the body which form the external structure of our bodies, the primary hip flexors — the iliacus and psoas — are internal and are situated deep in our core, tucked in behind our vital organs.
Considering what could negatively impact them, three common habits of modern life strike me as the most consequential:
1) long hours sitting in chairs and cars
The repetitive hours with the hip flexors in a shortened position, especially when we’re under stress, provides ample opportunity for these muscles to adapt into a locked short position.
2) constricted or paradoxical breathing
Paradoxical breathing occurs when the diaphragm muscle does not, or cannot, fully contract downward to pull a full breath into the lungs. This dysfunctional breathing is catalyzed by long hours of sitting, unchecked stress and abdominal clenching. The chronic intra-abdominal pressure that can result can cause ischemia (reduced blood flow) in the hip flexors leading to dysfunction.
Additional negative effects of paradoxical breathing include (but are not limited to):
→ Reduced blood flow to the vital organs
→ Reduced oxygen content in our blood
→ Perpetuation of the fight / flight / freeze response in our nervous system
→ The inability to take a full breath which, when extreme, can cause feelings of panic
→ Forward head posture due to muscular and fascial shortening through the front of the body
3) The absence of regular squatting
(Regular squatting such as is done many times a day in the non-industrialized world to go to the bathroom)
The weakness and inflexibility caused by the absence of this type of regular squatting can reinforce hip flexor dysfunction. Weakness in the quadriceps and the gluteus maximus, combined with excessive tightness in the hamstrings and the hip joints, creates an environment in which the hip flexor muscles can lock down unopposed by appropriate counter-balancing.
these forces are inextricably linked
As perhaps you can imagine or have even experienced, these three habits of modern life are often inextricably linked with one another, each mutually reinforcing the other two.
Also they go a long way in explaining, not only why hip flexor dysfunction and pelvic torsion are so widespread — even epidemic — but why a clear conventional medical diagnosis is not easy to come by.
These are complex functional problems that can’t be explained by looking at an X-ray or MRI or CAT scan.
Without seeing the whole and considering context, the root causes of much unexplained pain and a lot of mysterious symptoms cannot be easily understood, much less effectively treated.
While the problem of a twisted pelvis, or pelvic torsion, is extremely common, effective solutions are not plentiful.
That's why I felt it was essential to build a comprehensive program for this pervasive problem and why I developed the self-paced online course, "Postural Blueprint for Correcting Pelvic Torsion: The Complete Guide To Restoring Pelvic Balance."
How do you fix pelvic torsion? With the Postural Blueprint
Return to Top | Causes Index | Home Page
Anatomy Images Courtesy of BIODIGITAL
Stephen O'Dwyer, cnmt
Neuromuscular Therapist & Pain Relief Researcher
FOUNDERLower Back Pain Answers |

|
CURRENT COURSES POSTURAL BLUEPRINT FOR CORRECTING PELVIC TORSION: The Complete Guide To Restoring Pelvic Balance (2022) STRETCHING BLUEPRINT FOR PAIN RELIEF & BETTER FLEXIBILITY: The Complete Guide to Pain-Free Muscles Using Active Isolated Stretching (2020) HEALING THE HIDDEN ROOT OF PAIN: Self-Treatment for Iliopsoas Syndrome (2013) FREE MINI COURSE: Introduction to Active Isolated Stretching |
